
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI is changing everything, but what exactly is it? In 2025, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept. It’s a technology shaping how we live, work, and even think. From tools like ChatGPT and Grok to autonomous vehicles from Tesla and voice assistants in our homes, AI has rapidly integrated into everyday life. Financial services, education, and healthcare are all being transformed.
This guide will help readers understand the foundations of AI in a simple, structured way. You’ll explore what AI really means, how it operates behind the scenes, where it’s being applied globally, and even how AI is changing industries like Crypto.
Whether you're a newbie or simply curious, this beginner’s guide will provide clear, trustworthy answers to today’s most important AI questions.
How did Artificial Intelligence (AI) start?
Artificial Intelligence refers to machines that simulate human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, and decision-making. The term “Artificial Intelligence” was first coined in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, which marked the birth of AI as a field of study. Since then, progress has been steady and impactful:
- 1950s – Alan Turing proposed the “Turing Test”
- 1980s – Rise of expert systems
- 1997 – IBM’s Deep Blue beats chess champion Garry Kasparov
- 2011 – IBM Watson wins Jeopardy!
- 2020s – AI powers chatbots, autonomous cars, and medical diagnosis
AI isn’t just about robots. It’s a vast discipline covering:
- Narrow AI – Specialized tasks (e.g., facial recognition)
- General AI – Human-like cognitive capabilities
- Superintelligence – Hypothetical, surpassing human intelligence
How Does AI Work?
At its core, AI learns from data by analyzing patterns, making predictions, and improving over time. Organizations like OpenAI are leading research in general-purpose AI systems that can reason, write, and even create content. This intelligence manifests through several key subfields:
- Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms identify patterns and learn rules from datasets. For example, ML can predict credit scores or detect fraud.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML using neural networks with many layers. It excels at recognizing images, speech, and complex patterns.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Empowers AI to understand and generate human language. Chatbots and translation tools use NLP to interpret text and spoken words.
- Computer Vision: Enables machines to “see” by processing images and videos. AI can detect objects, faces, and medical conditions visually.
- Robotics: Combines AI with physical machines. Robots use AI to navigate environments, execute tasks, and adapt to change.
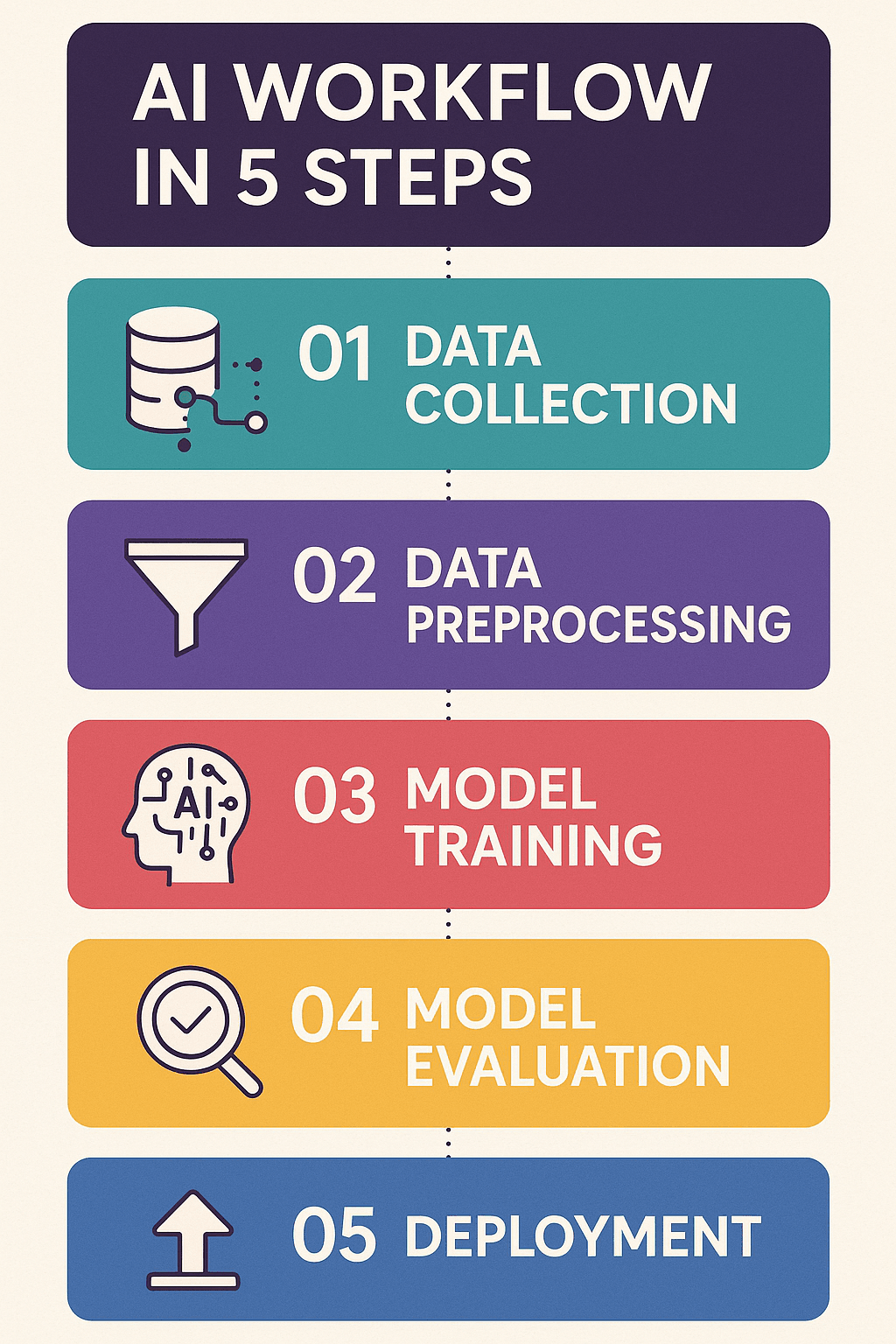
Together, these components allow AI to power modern applications from autonomous cars to virtual assistants by processing vast amounts of data intelligently and efficiently.
Popular AI Models – Chat GPT, Gemini, Grok, and more.
In 2025, several AI models have become household names due to their capabilities across industries. Each relies on specific AI concepts:
- ChatGPT (OpenAI) – Uses NLP and deep learning to generate human-like text.
- Grok (X AI) – Leverages NLP and contextual learning to integrate with platforms like X (formerly Twitter).
- DALL·E – Employs computer vision and deep learning to create images from text prompts.
- Gemini – Combines NLP and reinforcement learning for search and productivity tools.
- Claude – Focuses on safe NLP-based interaction with a strong emphasis on alignment and ethics.
- Tesla Autopilot – Utilizes deep learning and computer vision to navigate vehicles autonomously.
These models represent the diverse range of AI applications reshaping business, communication, and creativity.
Key Components of an AI System
Every Artificial Intelligence system relies on a set of fundamental components that enable it to function effectively. First and foremost is data, which serves as the foundational input. Without large, high-quality datasets, no AI model can learn or improve. Next are algorithms, or models, which are mathematical formulas and instructions used to process the data and recognize patterns.
Then comes the training process, where the AI system learns from the data through repeated exposure, gradually improving its performance. Lastly, a feedback loop is essential. It allows the system to compare its output with the expected result, adjust accordingly, and refine its accuracy. Together, these components make Artificial Intelligence adaptable, powerful, and increasingly capable of mimicking human decision-making.
Real-World Applications of AI in 2025
Artificial Intelligence is deeply embedded in nearly every major industry in 2025. Here are some key examples:
- Healthcare: AI supports diagnostics, predicts diseases, and aids drug discovery through massive data analysis.
- Crypto: It plays a vital role in trading strategies, powers trading bots, and enhances fraud detection and security protocols.
- Marketing: AI drives chatbots, ad targeting, content personalization, and campaign optimization.
- Transportation: Self-driving vehicles and smart traffic systems depend on AI for safety and efficiency.
- Manufacturing: Automation and robotics improve productivity, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management.
- Consumer Tech: Smart assistants, home automation, and IoT devices rely on AI for personalization and user commands.
From Crypto markets to hospital rooms, AI’s influence continues to grow in scale and sophistication.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Crypto Industry
The intersection of Artificial Intelligence and the Crypto Industry is reshaping how users interact with digital assets. AI enhances crypto trading by powering automated bots that analyze market trends in real-time, execute trades with precision, and reduce human error. It also improves risk assessment by processing vast data sets to detect patterns that signal price movements.
In addition, AI aids in fraud detection, identifying suspicious transactions and helping exchanges ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools enable sentiment analysis, giving traders insights from news and social media. Portfolio management also benefits from AI, allowing users to optimize asset allocation based on predictive modeling.
As the crypto ecosystem grows, AI is becoming an essential tool for improving decision-making, increasing security, and creating smarter, faster, and more efficient trading environments.
AI vs Machine Learning – What is the Difference?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way that we would consider “smart.” Machine Learning (ML), on the other hand, is a specific subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed.
Think of it like this: AI is the universe, and ML is a planet within it. AI includes everything from rule-based systems that follow predefined instructions, to neural networks and deep learning systems. Not all AI involves learning from data—some AI systems operate using decision trees or if-then rules without any learning at all.
While ML focuses on pattern recognition and predictive analytics, AI as a whole encompasses reasoning, planning, and language understanding. Both work together to power the intelligent systems we use today.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence brings numerous advantages across various industries, making systems smarter, faster, and more responsive. Key benefits include:
- Efficiency and automation – AI can handle repetitive tasks with minimal human intervention, saving time and costs.
- Accuracy and prediction – Machine learning models can analyze vast data sets and deliver high-accuracy predictions in fields like finance or healthcare.
- Scalability – AI systems can manage large-scale operations and adjust to increasing workloads without sacrificing performance.
- 24/7 availability – Unlike humans, AI systems can operate continuously, improving customer support and service delivery.
- Personalization – AI tailors content and recommendations based on individual behavior, improving user experience in e-commerce, entertainment, and more.
- Faster decision-making – AI analyzes data in real time, enabling quicker and more informed decisions.
- Data-driven insights – AI helps businesses extract meaningful insights from raw data, leading to better strategies and innovation.
Challenges and Risks of AI
While Artificial Intelligence offers impressive capabilities, it also raises several concerns that must be addressed. One of the most pressing issues is bias and fairness AI systems can unintentionally reinforce societal prejudices if trained on biased data.
Another challenge is job displacement, as automation threatens to replace human labor in certain industries. Privacy concerns also arise since AI systems often require access to vast amounts of personal data to function effectively.
Security threats, including the rise of deepfakes and AI-assisted hacking, pose serious risks to individuals and institutions alike.
Additionally, there is a growing concern about the lack of transparency in AI decision-making. Many advanced systems operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how conclusions are reached, which complicates accountability and trust. Addressing these challenges is crucial for safe and ethical AI development.
The Future of AI – What’s Next?
The future of Artificial Intelligence is advancing rapidly across multiple domains. According to the Stanford AI Index, global AI capabilities and funding have grown exponentially, with 2025 seeing record adoption in enterprise and education. Generative AI models are evolving to produce not just text, but also high-quality images, video, and even music, reshaping how content is created. Autonomous systems, such as drones and self-driving vehicles, continue to improve in reliability and adoption.
In the Crypto and financial sectors, AI is optimizing algorithmic trading, fraud detection, and decentralized governance. Human-AI collaboration tools are becoming more intuitive, enabling users to enhance creativity and productivity with real-time support. As capabilities expand, governments and institutions worldwide are moving to establish clearer regulations and ethical frameworks to ensure responsible use. The EU AI Act is one of the most comprehensive efforts to regulate AI, influencing how companies build and deploy AI technologies across the EU and beyond. These efforts aim to strike a balance between innovation and safety, securing AI’s role as a transformative tool for the future.
Summary – Why You Should Understand AI
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping industries, influencing how we live, work, and interact with technology daily. From automating repetitive tasks to enabling smart decision-making, AI offers practical solutions that are already transforming the global landscape.
It’s not just about futuristic robots, real-world applications in areas like healthcare, finance, transportation, and even Crypto trading make it relevant for everyone. Understanding AI means being better prepared for the opportunities and challenges it brings.
As AI continues to evolve, it’s crucial for individuals and organizations to stay informed and engaged. Whether you’re a student, investor, or tech user, knowing how Artificial Intelligence works and how it intersects with rapidly growing industries like Crypto is essential to thrive in 2025 and beyond.
